Tense and Aspect
Regular and Irregular Verbs
Regular verbs form their past form and the past
participle by adding -ed to the base form.
Examples: talk – talked watch – watched
Irregular verbs form their past form and past
participle without adding -ed to the base
form.
Examples: do – did sing – sang
Source: Lester, Mark. McGraw-Hill Education Handbook
of English Grammar & Usage. McGraw Hill Professional, 2018.
Tense
is a verb-based technique used to convey the timing of an action or state in
relation to the time of speaking, as well as occasionally its continuation or
completion.
There are three verb tenses: present, past, and past
participle.
·
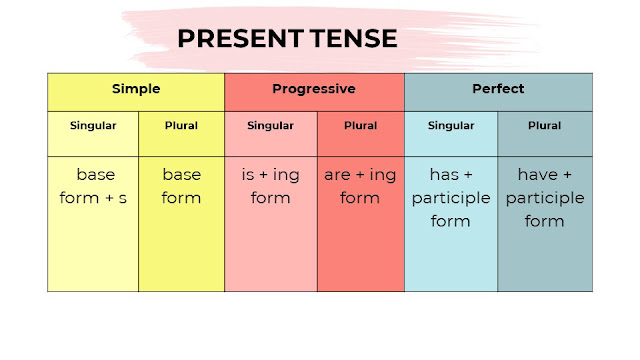
Present Tense
Simple Present Tense talks about present or habitual actions.
Example: Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
Progressive
Present Tense involves actions happening in the present while the doer is speaking
Example: Water is already boiling when I got the
pasta.
Present
Perfect Tense is for actions just done or still in effect.
Example: Water has boiled a minute ago.
· Past Tense
Simple
Past Tense - talks about actions
completed in the past.
Example:
I finished my homework.
Progressive
Past Tense - pertains to actions completed before some other past action.
Example:
I was still finishing my homework when you called.
Present
Perfect Tense - are for actions just
done or still in effect.
Example:
I had finished my homework since this weekend.
· Future Tense
Simple
Future Tense - talks about actions to be
done in the future.
Example:
Eddie will win the music competition.
Progressive
Future Tense - is for actions to happen in the future while the doer speaks.
Example:
Eddie will be winning the competition while I’m in medical school.
Present
Future Tense - are for actions to be
completed before some future time.
Example:
Eddie will have won the competition before you leave medical school.
II. Preposition
A small, yet very important part of
grammar is the preposition. A preposition is used to elaborate the action by
telling where or when it happens. Without prepositions, it would be hard for
English speakers to communicate locations, addresses, time, and dates. In the
CCS workplace, customer details are always spoken and written by both agent and
customers. Hence, it is crucial to know the differences between these
prepositions of place and time. This lesson will make you more aware of rules
in using prepositions.
Preposition Defined
A preposition is a word or set of words used before a
noun, pronoun, or noun phrase. It indicates direction, time, place, location, and spatial relationships, or introduces an object.
Preposition of Place
Prepositions of place refer to something or someone’s
located.
• At is used to discuss a certain point or a
specific address.
Example: at 123 Sunset Park, California
• In is used for an enclosed space, or wide, spacious
areas.
Examples: in a box in the building
• On is used for a surface such as roads, streets,
and bodies of water.
Examples: on the table on the train
• By is used when the object or person discussed is
only near a certain object or person.
Examples: by the sea by the house
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time allows you to discuss a specific
time period such as a date on the calendar, one of the days of the week, or the
actual time something takes place.
• At refers to clock times, holidays, and other very
specific time frames, such as “at night.”
Examples: at 7:00 PM at noon
• In is used to discuss months, seasons, years, centuries,
general times of day, and longer periods of time such as “in the past.”
Examples: in June in spring in 2019
• On is used for days of the week, specific dates,
and special days such as “on New Year’s Day.”
Examples: on Tuesday on January 25, 2018
• By is used to refer to dates of completions of an
action.
Examples: by March by 2020
Prepared by:
JOANNE V. CURA
Teacher I
Checked by:
CRISANTA F. CAUDAL

























Comments
Post a Comment